Guarantee Throughput with QoS: Ensuring Optimal Network Performance
In the increasingly interconnected digital landscape, network performance is paramount for businesses to maintain efficiency and productivity. Quality of Service (QoS) is a critical technology that helps manage and optimize network traffic, ensuring that essential applications receive the necessary bandwidth and maintain consistent performance. This article explores how QoS works, its benefits, and practical applications, providing insights into how businesses can guarantee throughput and optimize their network infrastructure.
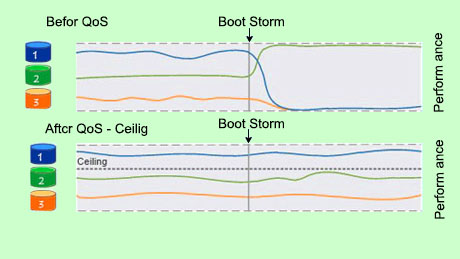
Understanding Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to a set of technologies and techniques used to manage and prioritize network traffic to ensure a certain level of performance for critical applications and services. QoS helps to minimize latency, jitter, and packet loss, which are crucial for maintaining the quality of voice, video, and data transmissions.
Key Components of QoS
- Traffic Classification: Identifying and categorizing different types of network traffic based on their specific requirements.
- Traffic Shaping: Regulating the flow of traffic to ensure that the network does not become congested.
- Bandwidth Management: Allocating the appropriate amount of bandwidth to different types of traffic to meet their performance needs.
- Priority Queuing: Prioritizing certain types of traffic to ensure that critical applications receive the necessary resources.
- Traffic Policing: Enforcing traffic policies to prevent any single application or user from consuming excessive bandwidth.
How QoS Guarantees Throughput
Throughput refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted through a network over a given period. Ensuring consistent and reliable throughput is essential for maintaining the performance of time-sensitive applications such as VoIP, video conferencing, and online gaming. QoS helps guarantee throughput by:
1. Prioritizing Critical Traffic
QoS allows network administrators to prioritize critical traffic over less important data. For instance, real-time applications like VoIP and video conferencing can be given higher priority over file downloads or web browsing. This ensures that critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and maintain optimal performance.
2. Managing Bandwidth Allocation
By implementing bandwidth management policies, QoS ensures that each application receives an appropriate amount of bandwidth based on its requirements. This prevents any single application from monopolizing the available bandwidth and ensures a fair distribution of resources.
3. Reducing Network Congestion
Traffic shaping and policing techniques help to prevent network congestion by controlling the flow of data. By smoothing out bursts of traffic and enforcing bandwidth limits, QoS ensures that the network remains stable and performs optimally even under heavy load.
4. Minimizing Latency and Jitter
Latency and jitter can significantly impact the performance of real-time applications. QoS helps to minimize these issues by prioritizing critical traffic and ensuring that data packets are transmitted in a timely and orderly manner.
Benefits of Implementing QoS
1. Improved Application Performance
By prioritizing critical traffic and ensuring that applications receive the necessary bandwidth, QoS enhances the performance of time-sensitive applications. This leads to better user experiences and increased productivity.
2. Enhanced Network Reliability
QoS helps to prevent network congestion and minimize latency, jitter, and packet loss. This leads to a more reliable network that can consistently meet the performance requirements of critical applications.
3. Efficient Bandwidth Utilization
QoS ensures that bandwidth is allocated efficiently based on the specific needs of different applications. This prevents wastage of resources and ensures that the available bandwidth is used effectively.
4. Better User Experience
By guaranteeing throughput and maintaining the performance of critical applications, QoS enhances the overall user experience. Users can enjoy smooth and uninterrupted access to essential services, leading to increased satisfaction and productivity.
Practical Applications of QoS
1. VoIP and Video Conferencing
Voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing applications require low latency and minimal jitter to function effectively. QoS helps to prioritize these applications, ensuring that voice and video data is transmitted smoothly and without interruption.
2. Online Gaming
Online gaming is highly sensitive to latency and packet loss. QoS ensures that gaming traffic is prioritized, providing gamers with a stable and responsive connection.
3. Streaming Media
Streaming media applications, such as video on demand (VoD) and live streaming, require consistent bandwidth to deliver high-quality content. QoS helps to allocate the necessary bandwidth, preventing buffering and ensuring a smooth viewing experience.
4. Enterprise Applications
Many enterprise applications, such as Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, require reliable and consistent network performance. QoS ensures that these applications receive the necessary resources to function effectively.
5. Cloud Services
As businesses increasingly rely on cloud services, maintaining consistent network performance is crucial. QoS helps to manage the flow of data between on-premises infrastructure and cloud services, ensuring reliable access to critical applications and data.
Implementing QoS in Your Network
1. Assess Your Network Traffic
Before implementing QoS, it is essential to understand the specific needs of your network. This involves analyzing network traffic to identify critical applications and their performance requirements.
2. Define QoS Policies
Based on your assessment, define QoS policies that prioritize critical traffic and allocate bandwidth accordingly. This involves setting traffic classes, defining priority levels, and specifying bandwidth limits.
3. Configure Network Devices
Implementing QoS requires configuring network devices such as routers and switches to enforce the defined policies. This involves setting up traffic classification, shaping, and policing rules on each device.
4. Monitor and Adjust
Once QoS is implemented, continuously monitor network performance to ensure that the policies are effective. Make adjustments as needed to address any issues and optimize performance.
Conclusion
Quality of Service (QoS) is an essential technology for managing and optimizing network traffic. By prioritizing critical applications, managing bandwidth allocation, and reducing network congestion, QoS helps to guarantee throughput and maintain optimal network performance. Whether you are running VoIP, video conferencing, online gaming, or enterprise applications, implementing QoS can significantly enhance the reliability and efficiency of your network. As businesses continue to rely on digital services, ensuring consistent and reliable network performance through QoS will be crucial for maintaining productivity and achieving success in the digital age.